Overview
Leverage retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to gain conversational insights from PDFs. This project demonstrates the power of RAG systems for extracting information from documents without the need for expensive fine-tuning.
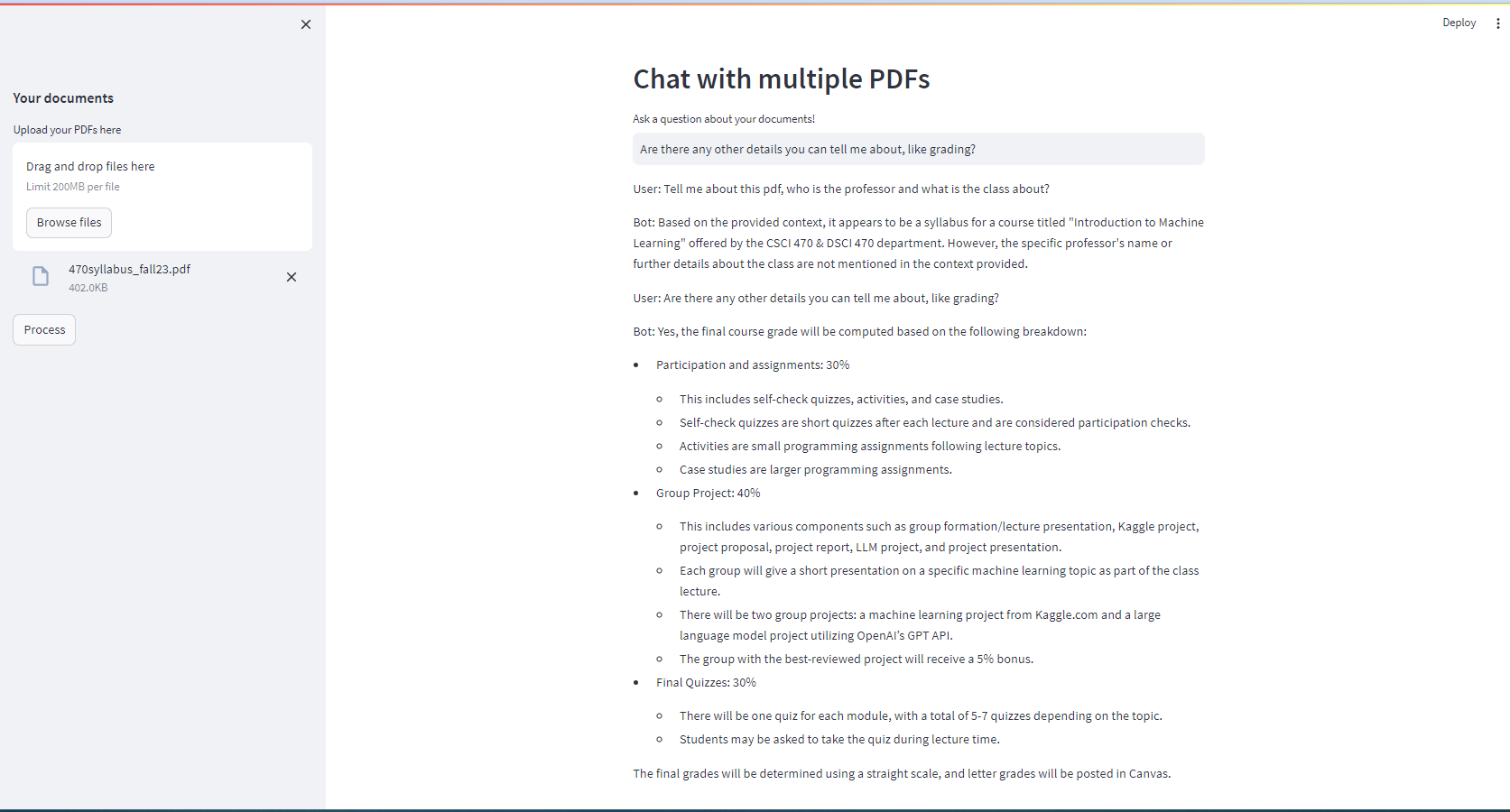 A screenshot of the application being locally hosted and returning context-aware responses for an uploaded ‘Intro to Machine Learning’ syllabus.
A screenshot of the application being locally hosted and returning context-aware responses for an uploaded ‘Intro to Machine Learning’ syllabus.
Inspiration
This project was inspired by the Fine-tuning vs RAG episode of the Practical AI Podcast. Guest Demetrios Brinkmann discusses his strong opinion on the matter - expressing some compelling arguments for why he believes RAG is an overlooked aspect of NLP implementation.
”… you think ‘Oh, well, if I just fine-tune an LLM on all of my emails, then the LLM will know how to write emails like me.’ But it’s not like that. There’s the misconception that it’s not like equal in that regard. Fine-tuning - you don’t fine-tune something so that it can understand you more… that’s where retrieval-augmented generation shines. Because you just say, ‘Hey, here’s a database, or a vector database of all of Demetrios’ emails’, and you can do some few-shot prompting and say ‘Write like this. Here’s five styles of Demetrius writing a response to this, so make a sixth one.’ And you’re golden. You don’t need to go through like burning a lot of cash on GPUs - and GPUs are scarce these days - to fine-tune some model that may or may not work after you’ve fine-tuned it.” — DEMETRIOS BRINKMANN
Implementation
Coincidentally, I had been exploring the idea of building a chatbot for PDF documents and came across a well-made tutorial by Alejandro AO. The final product is a slightly configurable, locally hostable chatbot that effectively leverages local vector storage with FAISS.
App Architecture
The Streamlit-hosted webapp provides a simple interface for uploading PDF documents and receiving interactive question-answering based on the uploaded contents:
- Uploading PDFs: The application accepts multiple PDF files through a user-friendly sidebar interface
- Text Extraction: Upon processing, the app extracts text from each page using PyPDF2’s PdfReader
- Text Chunking: The full text is split into chunks with overlaps to preserve semantic meaning across boundaries
- Vector Embedding: Text chunks are converted into vector embeddings using HuggingFace or OpenAI embeddings, then stored and indexed using FAISS for efficient retrieval
- Interactive Chat: A ConversationalRetrievalChain links the language model, memory buffer, and retriever to enable the interactive session
- Conversation Management: User input is processed through the conversation chain to generate context-aware responses
Key Technologies
- FAISS: Fast vector similarity search for efficient document retrieval
- LangChain: Framework for building LLM applications
- Streamlit: User-friendly web interface
- PyPDF2: PDF text extraction
- HuggingFace/OpenAI Embeddings: Vector embeddings for semantic search
Conclusion
Understanding RAG systems is paramount in the modern AI landscape. They act as intelligent architects that enrich LLMs with precise, contextually relevant information drawn from expansive datasets - offering a compute-efficient alternative to fine-tuning.
Vector storage stands as the cornerstone of efficient data retrieval, especially for semantic meaning and contextual relevance. Implementing these storage methods using high-level abstractions like the FAISS library allows us to query and retrieve complex information with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
This venture into RAG and vector storage is about more than just staying up-to-date on current trends; it’s about actively contributing to the evolution and democratization of AI.