Overview
A comprehensive collection of computer vision projects exploring various techniques from classical computer vision to deep learning. Project code may not be public due to IP, unpublished research, or academic integrity considerations.
Augmented Reality with Planar Homographies
Homographies are a powerful tool in computer vision to map points from one camera view to another. This can be used to stitch images together and overlay images on top of each other.
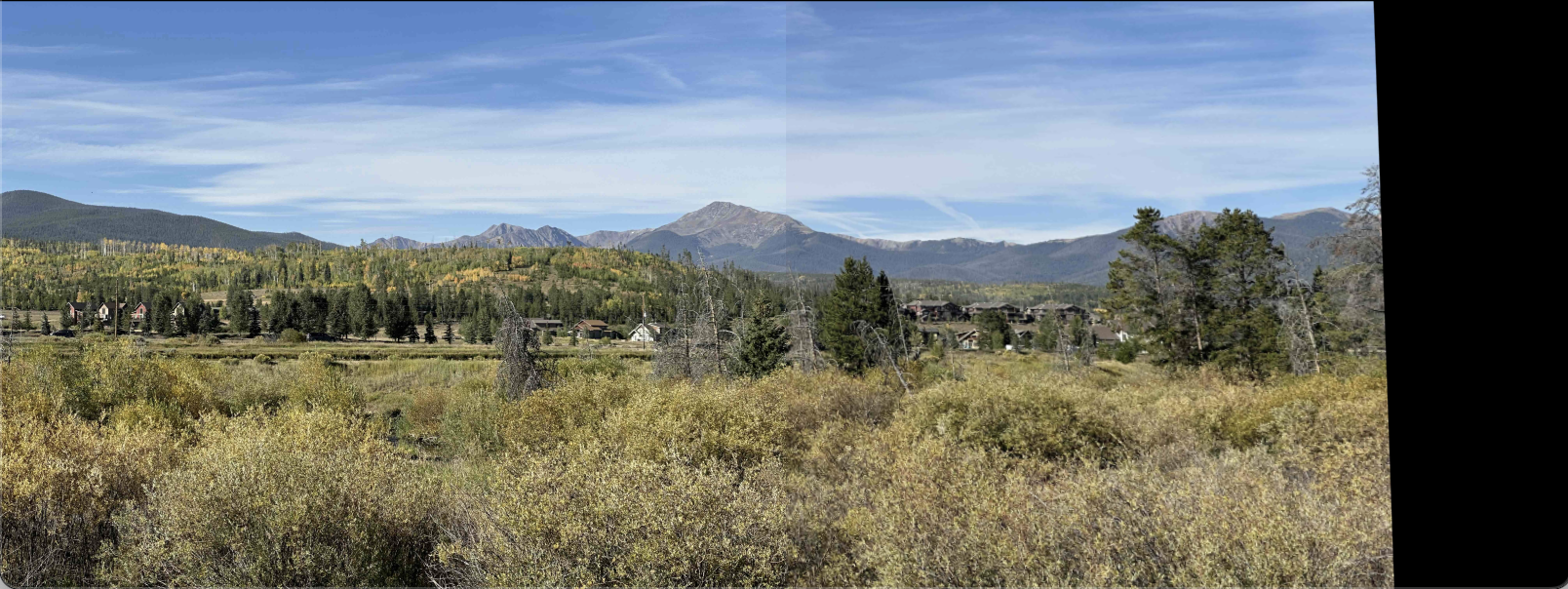
Image Stitching
I took two images of Buyers Peak in Winter Park, CO separated by pure rotation (using the same camera). Using RANSAC to identify keypoints between the images, I was able to estimate the homography matrix and stitch the images together.

Video Overlay
I used a reference photo of a book cover to map video frames onto a moving view of the same book. The homography is computed for each frame, enabling real-time AR overlay. Optimization could be achieved through multithreading or computing the homography every k frames.
Lucas-Kanade Object Tracking
Developed at CMU, Lucas-Kanade tracking is a method for tracking objects in video via optical flow. By modeling frame-to-frame changes as 2D warps, we can solve for a pure translation warp function given a template offset.
The implementation demonstrates the value of template correction when handling object occlusion, rotational changes, and scale changes.
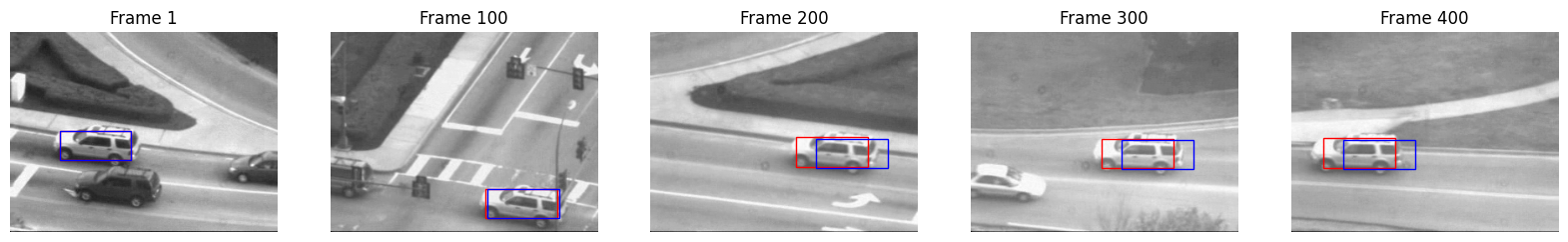

Note: This method is not robust to large changes in scale or rotation.
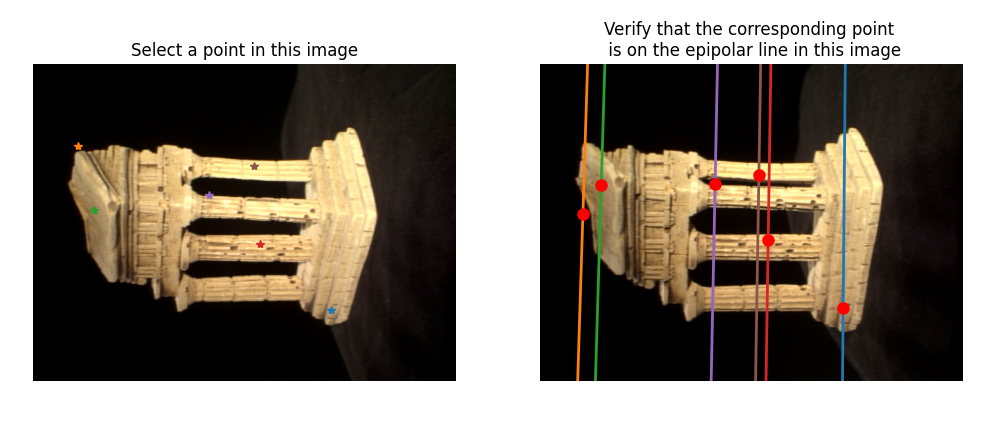
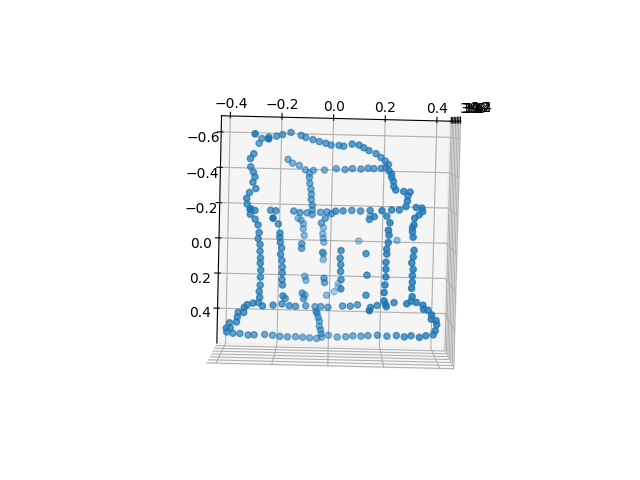
3D Reconstruction
Two stereo-separated cameras can be used to reconstruct 3D scene estimates by identifying corresponding points in both images. This process involves:
- Determining epipolar lines in one image
- Searching for corresponding points in the other image
- Constructing the essential matrix via camera intrinsics and the fundamental matrix (derived via the eight-point algorithm)
- Estimating camera pose and 3D structure

Homebrew CNN for OCR
Built a convolutional neural network from scratch for optical character recognition (OCR). The CNN was trained on the MNIST dataset and tested on a custom dataset of handwritten characters.
Key achievements:
- 98% accuracy on custom dataset
- Complete implementation without high-level frameworks
- Integration with character recognition and preprocessing pipeline
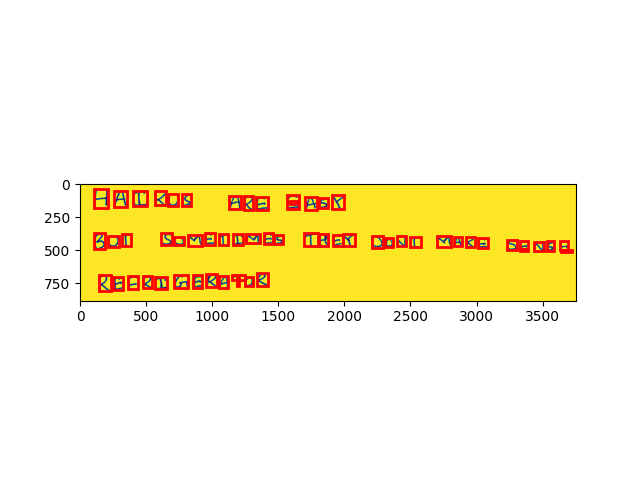
This project is similar to my Neural Networks from Scratch project, but instead of approximating the AND function, I built a CNN specifically for optical character recognition.
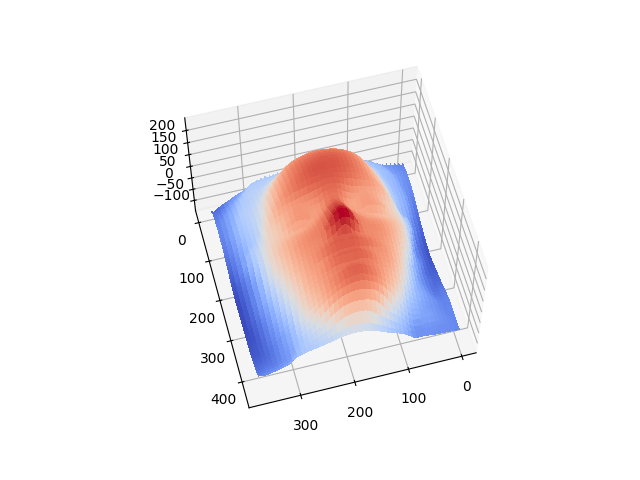
Photometry (Physics-Based CV)
Using known light sources and directions, we can reconstruct albedos and normals to estimate the shape of an object. This physics-based approach to computer vision demonstrates how lighting information can be leveraged for 3D shape estimation.

Future Directions
Moving forward, I’m particularly interested in:
- Text-to-image generation and fine-tuning (Flux.1 LoRA)
- Real-time computer vision applications
- Integration of classical CV techniques with deep learning